Blog
CERVICAL SPONDYLITIS
by
Dr. Sushmitha AR
on
Aug 08, 2024
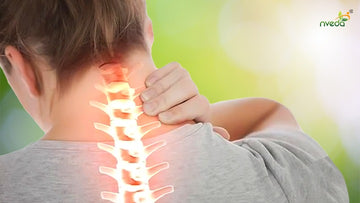
The cervical vertebrae are the uppermost part of the vertebral column located in the neck region. There are seven cervical vertebrae, labeled C1 through C7. These vertebrae are connected to each other by intervertebral discs, which provide cushioning and facilitate movement.
Cervical spondylitis, also known as cervical spondylosis, is a degenerative condition affecting the cervical spine, This condition primarily arises due to age-related changes in the intervertebral discs and joints, leading to the development of osteophytes (bone spurs), disc degeneration, and loss of spinal structure integrity.
Causes
-
Aging: The most common cause, as the discs and joints in the cervical spine degenerate over time.
-
Herniated Discs: Discs can become dehydrated and shrink, leading to herniation.
-
Bone Spurs: Extra bone can grow on the spine, which can compress the spinal cord or nerve roots.
-
Injury: Past neck injuries can predispose one to spondylosis.
-
Genetics: A family history of neck pain or osteoarthritis can increase the risk.
Risk Factors
-
Age - The condition is more common in individuals over the age of 50 as the intervertebral discs and other spinal structures naturally degenerate over time.
-
Family History: A family history of cervical spondylitis or other degenerative spinal conditions can increase the risk of developing the disease. Genetic factors can influence the rate of disc degeneration and the development of bone spurs
-
Repetitive Strain: Jobs that involve repetitive neck movements, heavy lifting, or prolonged periods of poor posture (such as desk jobs) can contribute to the wear and tear of the cervical spine.
-
Manual Labor: Occupations requiring heavy lifting or physically demanding tasks can accelerate spinal degeneration.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can weaken the muscles that support the cervical spine, leading to increased strain and wear on the vertebrae and discs.
-
Poor Posture: Poor posture, especially when sitting for long periods, can put additional stress on the cervical spine, contributing to degenerative changes.
-
Smoking: Smoking has been linked to accelerated disc degeneration due to reduced blood flow to the discs and overall decreased spinal health.
-
Previous Neck Injuries: A history of neck injuries, such as whiplash, can predispose individuals to cervical spondylitis. These injuries can damage the vertebrae, discs, and ligaments, leading to premature degeneration.
-
Excess Weight: Carrying excess body weight can put additional strain on the spine, including the cervical region, accelerating the degenerative process.
-
Osteoarthritis: Individuals with osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease, are more likely to develop cervical spondylitis due to similar degenerative processes affecting the joints in the spine.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: This autoimmune condition can also affect the cervical spine, leading to inflammation and degeneration.
Symptoms
- Headaches : Often originating from the neck.
- Neck Pain and Stiffness
- Shoulder, Arm, or Hand Pain: Caused by nerve compression.
- Weakness and Numbness: In the arms, hands, legs, or feet if the spinal cord is affected.
- Loss of Balance: Difficulty walking if there is significant spinal cord compression.
- Muscle Spasms: In the neck and shoulder muscles.
- Tingling, numbness and weakness in the arms, hands, legs or feet
- Loss of bowel/ bladder control
Diagnosis
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Assessing symptoms and examining the neck, shoulders, arms, and legs.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to visualize the spine and any degenerative changes.
- Electromyography (EMG): To check the function of the nerves.
Preventive Measures
- Maintain Good Posture: Especially during activities like sitting at a desk, using a computer, or reading.
- Regular Exercise: Focus on strengthening neck and back muscles and maintaining flexibility.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensuring that workspaces are set up to avoid strain on the neck.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: To reduce stress on the cervical spine